Gravitational potential energy (GPE) is the energy stored in an object due to its height above a reference point. It depends on three main factors:
- Mass of the object (m)
- Height from the ground (h)
- Gravitational acceleration (g = 9.81 m/s² on Earth)
Statement
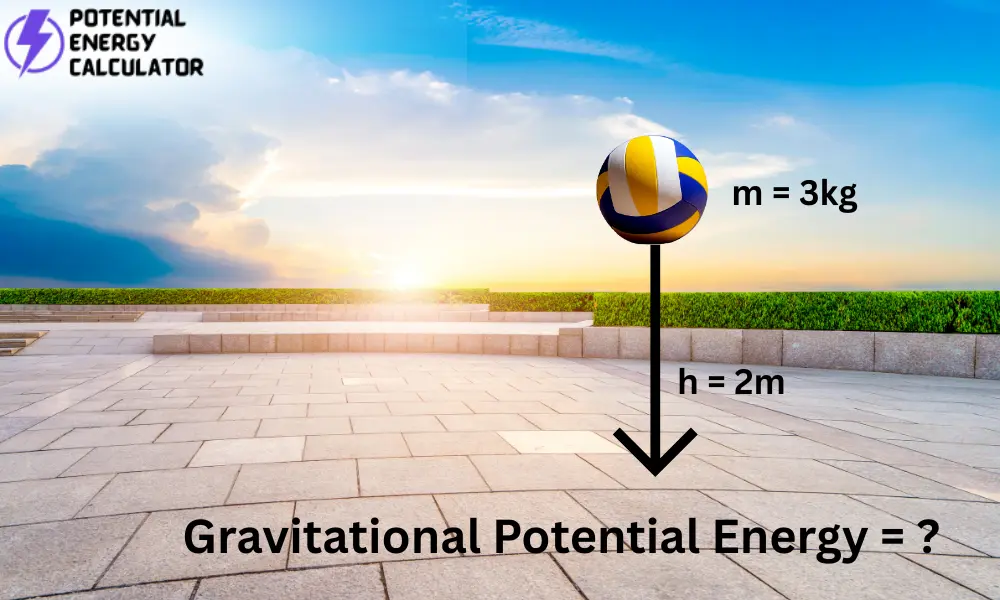
Calculate the gravitational potential energy stored in a 3 kg object placed 2 meters above ground level.
Use g = 9.81 N/kg and round the final answer to 1 decimal place (1dp).
Data (Given Values)
From the question, the given values are:
- Mass of the object (m) = 3 kg
- Height above ground (h) = 2 m
- Acceleration due to gravity (g) = 9.81 m/s²
Required (To Find)
We need to calculate the gravitational potential energy (PE) of the object and round the final answer to 1 decimal place (1dp).
Formula to Use
The standard formula for gravitational potential energy (GPE) is:
GPE = mghwhere:
- G.P.E. = Gravitational Potential Energy (Joules, J)
- m = Mass (kg)
- g = Acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s²)
- h = Height (m)
Solution:
We are given:
- Mass (m) = 3 kg
- Height (h) = 2 m
- Acceleration due to gravity (g) = 9.81 N/kg
Step 1: Write the formula
GPE = mgh
Step 2: Substitute the given values
GPE = 3 × 9.81 × 2
Step 3: Perform the calculations
GPE = 3 × 19.62
GPE = 58.86 J
Step 4: Round to One Decimal Place (1dp)
GPE = 58.9 J
Final Answer: The gravitational potential energy stored in the object is 58.9 Joules (J) (rounded to 1 decimal place).
Result
Thus, the gravitational potential energy stored in a 3 kg object placed 2 meters above the ground is:
GPE = 58.9 J (1dp)Description & Explanation
Understanding the Concept
Gravitational potential energy (GPE) is the stored energy of an object due to its position above the ground. The higher the object and the greater its mass, the more potential energy it has.
In this case, we calculated the energy stored in a 3 kg object positioned 2 meters above the ground under Earth’s gravity (9.81 N/kg).
Step-by-Step Breakdown
- Identifying the Given Values
- Mass = 3 kg, Height = 2 m, and g = 9.81 N/kg.
- Substituting Values into the Formula
- We used the standard potential energy equation:
PE = mgh - Then, We substituted the values:
PE = 3 × 9.81 × 2
- We used the standard potential energy equation:
- Performing Multiplication
- 9.81 × 2 = 19.62
- 3 × 19.62 = 58.86 J
- Final Answer Rounded to One Decimal Place
- The final answer is 58.9 Joules (J), which represents the energy stored in the object due to its height above ground.
Real-Life Applications of Gravitational Potential Energy
The gravitational potential energy formula is widely used in physics and engineering for various real-world applications, including:
- Hydropower Plants: Water stored at high levels in dams has potential energy, which converts into kinetic energy to produce electricity.
- Cranes in Construction: Heavy materials lifted by cranes have potential energy before being lowered.
- Roller Coasters: At the highest points, roller coasters have maximum stored energy before moving downward.
- Weightlifting & Sports: A weightlifter holding weights above their head stores energy before lowering them.
Final Thoughts
This numerical problem demonstrates how to calculate gravitational potential energy step by step. The PE = mgh formula is a fundamental concept in physics and real-world applications.
If you want to calculate gravitational potential energy instantly, try our Potential Energy Calculator for fast and accurate results.

